one|Lesson 51~60
Lesson 51~52
✨课文

✨单词
⚡本课重点
what...like:用来询问事物的状况,或询问人物、事物的外观、特征
e.g. What's the weather like today?、What's your house like?
how often:常用于对某事、动作发生的频率进行提问
e.g. How often do you go to the cinema?
频率副词:always > often > usually > sometimes > never
- 在句子中用于
be动词之后 - 用在实义动词之前
- 如果是否定句或疑问句,用在助动词和实义动词之间
- 为表示强调,频率副词可以放在句首或句尾
Lesson 53~54
✨课文
✨单词
⚡本课重点
like的不同词性
当其做动词时表示「喜欢、想要」
e.g. I like that sweet girl.
当其做介词时表示「怎么样、像...一样」
e.g. His car is like mine.
当其做形容词时表示「类似的、相似的」
Lesson 55~56
✨课文
✨单词
⚡本课重点
本节课主要还是围绕着一般现在时进行展开,只是着重使用一般现在时来表示某种习惯的、反复的动作
e.g. In the morning, Mr. Sawyer goes to work and the children go to school.
take sb. to somewhere:带某人去某处
e.g. Their father takes them to school every day.
Lesson 57~58
✨课文
✨单词
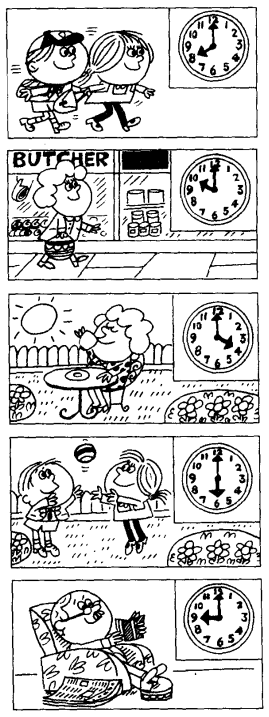
时间的表达方式
⚡本课重点
时间的表达方式
通用表达
e.g. six o'clock => 6点整、ten ten => 10点10分、twelve forty => 12点40分
分 past 时:表示「某个整点时间过去了多少分钟」,这种方式要求当前的自然分钟数必须
小于等于30e.g. half past six => 6点半、a quarter past ten => 10点15分、five past twelve => 12点5分
分 to 时:表示「距离某个整点时间还差多少分钟」,这种方式要求当前的自然分钟数必须
大于30e.g. ten to seven => 6点50分、a quarter to eleven => 10点45分
在口语环境中,当谈话双方对当前的时间都有个大致的掌握时,可以省略掉介词
to。例如:差15分钟就1点 =>quarter one
一般现在时与现在进行时
一般现在时表达「习惯或反复的动作」时,通常与时间频率副词连用
e.g.
always、often、usually、sometimes、never现在进行时表达「此刻正在进行的事情或动作」时,通常与时间状语连用
e.g.
now、at the moment、today、this morning、tonight等
Lesson 59~60
✨课文

✨单词
have用法①
⚡本课重点
have用法①:单词本义为「有、拥有」。它作为动词时有第三人称单数形式has,当它表示「有」这个概念时,其否定形式和疑问形式各有两种。
否定句:可以在
have/has后面直接加not,也可以用助动词do/does的否定形式。have not=haven't,has not=hasn't- e.g. I have a car. => I haven't a car. => I don't have a car.
- e.g. He has a car. => He hasn't a car. => He doesn't have a car.
一般疑问句:将
have/has提到句首(主语前面),或者用助动词do/does- e.g. Have you a car? => Do you have a car?
- e.g. Has he a car? => Does he have a car?
have的另外三种用法参考61~62课、81~82课和87~88课
else:常常跟在疑问代词、不定代词、疑问副词的后面
e.g. What else do you want?、Who else is from Japan?